Waste Management in Environmental Technology: An Informative Perspective
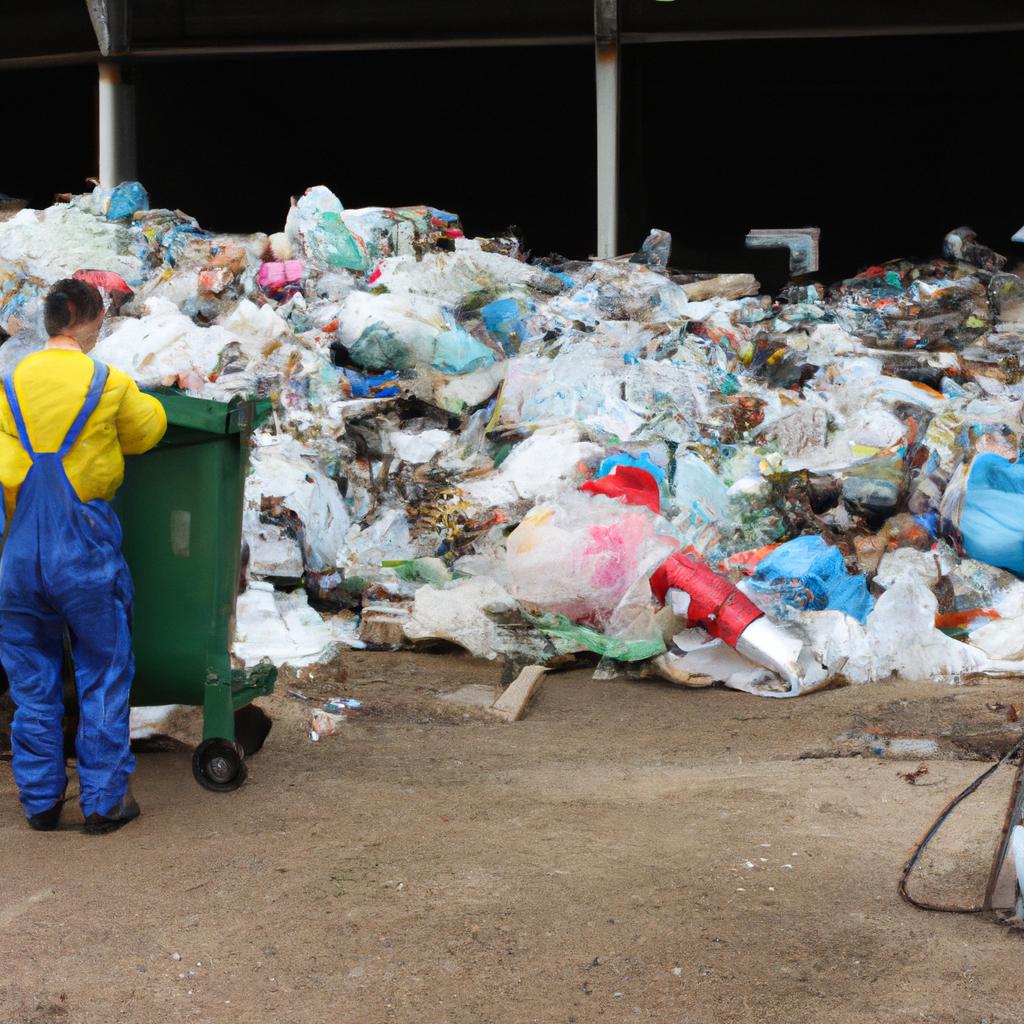
Waste management plays a crucial role in environmental technology, serving as the cornerstone for sustainable development and ecological conservation. Effective waste management practices are essential to mitigate the adverse impacts of human activities on the environment and public health. For instance, let us consider an urban area where improper waste disposal has resulted in contaminated water sources. In this hypothetical scenario, untreated waste is discharged directly into rivers and streams, leading to pollution that adversely affects aquatic ecosystems and poses serious threats to human well-being.
Environmental technology encompasses various strategies and techniques aimed at minimizing waste generation, optimizing resource utilization, and promoting responsible disposal methods. The field spans across multiple sectors including energy production, agriculture, manufacturing industries, and urban planning. With rapid industrialization and population growth, the need for efficient waste management systems has become even more critical. It demands innovative approaches that go beyond traditional waste treatment methods by focusing on prevention through recycling initiatives, reducing landfill usage, and harnessing renewable energies from waste materials.
Through this article, we aim to provide an informative perspective on waste management within the context of environmental technology. By examining current challenges faced in waste management practices and exploring emerging technologies and best practices globally, we can gain valuable insights into how these advancements contribute towards creating a cleaner and healthier planet. Additionally, we will also discuss the importance of public awareness and education in promoting responsible waste management practices. It is essential for individuals to understand their role in reducing waste generation, separating recyclable materials, and adopting sustainable consumption habits.
Moreover, we will delve into the concept of circular economy, which emphasizes the idea of a closed-loop system where resources are continuously reused and recycled. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates economic opportunities and promotes environmental sustainability.
Furthermore, we will explore the role of governments and policymakers in implementing effective waste management policies and regulations. Collaboration between various stakeholders including industry players, local communities, and non-governmental organizations is crucial to address the complex challenges associated with waste management.
In conclusion, by adopting innovative technologies, raising public awareness, and implementing comprehensive waste management strategies, we can pave the way towards a more sustainable future. Environmental technology plays a vital role in ensuring that our waste is managed responsibly, minimizing its impact on the environment while maximizing resource efficiency. Through collective efforts at individual, community, corporate, and governmental levels, we can make significant progress towards achieving a cleaner and healthier planet for future generations.
The Importance of Recycling
Recycling plays a crucial role in waste management, as it helps to mitigate the negative environmental impacts associated with improper disposal and excessive consumption. To illustrate this point, let us consider an example: Imagine a neighborhood where residents do not practice recycling. In this scenario, all types of waste are indiscriminately thrown into a single bin and sent to landfills. As a result, valuable resources such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal end up buried underground or incinerated, leading to significant environmental consequences.
Recognizing the importance of Recycling is essential for addressing these challenges and striving towards sustainable development. By actively participating in recycling efforts, individuals can contribute to several positive outcomes:
- Conservation of natural resources: Recycling reduces the need for extracting raw materials from the Earth’s limited reserves. For instance, reusing aluminum cans through recycling saves energy equivalent to manufacturing 20 new ones.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: When items are recycled instead of being disposed of in landfills or burned in incinerators, fewer greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere. This reduction directly contributes to combating climate change by minimizing carbon dioxide equivalents emitted during production processes.
- Energy savings: Recycling requires less energy compared to producing goods from virgin materials. For instance, manufacturing products from recycled plastics uses approximately two-thirds less energy than making them from new plastic.
- Job creation and economic benefits: The recycling industry provides employment opportunities at various stages, including collection, sorting, processing, and distribution. Moreover, it stimulates local economies by converting waste into valuable commodities that can be sold domestically or exported.
To further emphasize the significance of recycling in waste management practices, let us examine the following table:
| Waste Material | Amount Thrown Away (per year) | Recyclable Percentage | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper | 68 million tons | 67% | Conserves forests and reduces water pollution |
| Plastic | 30 million tons | 9% | Reduces dependency on fossil fuels and marine pollution |
| Glass | 11 million tons | 26% | Saves energy during manufacturing process |
| Aluminum | 3.7 million tons | 55% | Decreases mining activities and saves energy |
As shown above, substantial quantities of valuable materials are wasted each year due to inadequate recycling practices. By embracing recycling, we can significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with these discarded resources.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “The Benefits of Composting,” it becomes evident that recycling is just one facet of waste management. Another essential aspect lies in composting organic waste, which offers unique advantages for both the environment and society as a whole.
The Benefits of Composting
From the importance of recycling, we now turn our attention to another crucial aspect of waste management: composting. Composting is a natural process that involves the decomposition of organic materials into nutrient-rich soil amendments. This section will explore the benefits of composting and its role in sustainable waste management.
To illustrate the impact of composting, let’s consider a hypothetical case study. Imagine a small community garden struggling with poor soil quality due to years of chemical fertilizer use. By implementing a composting program, where residents contribute their food scraps and yard waste, this community can transform its barren soil into fertile ground for growing fruits and vegetables. Not only does this enhance local food production but also reduces reliance on synthetic fertilizers, minimizing environmental pollution.
Composting offers several significant advantages for both individuals and communities alike:
- Waste reduction: Composting diverts organic waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions—a potent greenhouse gas—and prolonging landfill lifespan.
- Soil enrichment: Compost improves soil structure by increasing water retention capabilities and enhancing nutrient content, leading to healthier plants and increased agricultural productivity.
- Carbon sequestration: The carbon stored within composted organic matter remains locked in the soil, mitigating climate change effects by reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
- Cost savings: Incorporating compost into landscaping or farming practices can decrease the need for commercial fertilizers and pesticides while saving money on waste disposal fees.
The emotional connection to composting becomes apparent when we examine the positive outcomes it generates. Consider the following table showcasing the various benefits associated with composting:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions; conserves landfill space |
| Agricultural | Enhances plant growth; increases crop yields |
| Economic | Saves money on waste disposal fees; reduces dependence on synthetic fertilizers |
| Community | Encourages local engagement; fosters sustainability mindset |
In summary, composting presents a sustainable solution to waste management. By diverting organic waste from landfills and turning it into nutrient-rich soil amendments, we can enhance agricultural practices, reduce environmental impact, and foster community engagement. Now, let’s explore effective methods for further reducing waste in the subsequent section on “Effective Methods for Waste Reduction.”
Effective Methods for Waste Reduction
Transitioning from the previous section on the benefits of composting, we now turn our attention to effective methods for waste reduction. While composting offers an excellent solution for organic waste management, it is crucial to explore additional strategies that can address other types of waste and contribute further towards sustainable environmental practices.
To illustrate this point, let us consider a hypothetical scenario in which a small urban community aims to reduce its overall waste production. By implementing various Waste reduction measures, such as recycling programs and promoting conscious consumer choices, the community successfully decreases its landfill-bound waste by 30% within six months. This example demonstrates how proactive waste management initiatives can have significant impacts on minimizing environmental harm caused by excessive disposal.
When considering effective methods for waste reduction, several key approaches emerge:
- Recycling: Implementing comprehensive recycling programs enables communities to divert recyclable materials away from landfills and redirect them into productive reuse cycles.
- Waste minimization at the source: Encouraging individuals and businesses to adopt practices that prioritize reducing unnecessary packaging or opting for reusable alternatives helps decrease overall waste generation.
- Education and awareness campaigns: Raising public consciousness about responsible consumption habits and the importance of proper waste segregation fosters a culture of sustainability.
- Extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs: Holding manufacturers accountable for managing their products’ lifecycle encourages them to design more eco-friendly options and take responsibility for their post-consumer impact.
By employing these strategies in combination with composting efforts, communities can significantly reduce their ecological footprint while fostering a sense of collective responsibility towards preserving the environment.
| Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling | Diverting recyclable materials from landfills; creating new raw materials | Conservation of resources; reduced energy consumption |
| Source Minimization | Adopting practices that minimize unnecessary packaging | Lessens resource depletion; reduces landfill space |
| Education Campaigns | Raising awareness about conscious consumption habits | Encourages behavioral change; promotes sustainability |
| EPR Programs | Holding manufacturers accountable for product lifecycle | Fosters eco-design; reduces waste generation |
In summary, effective waste reduction methods encompass a range of strategies such as recycling, source minimization, education campaigns, and extended producer responsibility programs. Implementing these approaches in conjunction with composting efforts can yield significant environmental benefits. By reducing waste at its source and diverting materials away from landfills, communities can work towards building more sustainable futures.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on “Exploring Alternatives to Landfills,” it is important to consider additional waste management solutions that complement the aforementioned techniques and further contribute to sustainable practices.
Exploring Alternatives to Landfills
Waste management is a critical aspect of environmental technology, as it involves the effective handling and disposal of waste materials to minimize their impact on the environment. In this section, we will explore alternative methods for waste reduction, highlighting their potential benefits and drawbacks.
One illustrative example of an effective waste reduction method is the implementation of recycling programs in communities. For instance, let us consider a hypothetical case study where a town introduced comprehensive recycling initiatives that encouraged residents to separate recyclable materials from general waste. This approach not only reduced the amount of waste being sent to landfills but also promoted resource conservation by reusing valuable materials such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
- Reducing landfill usage helps preserve natural habitats
- Recycling conserves energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Proper waste disposal prevents water contamination
- Waste-to-energy technologies can generate renewable power
In addition to these measures, exploring alternatives to traditional landfills is another important avenue worth considering. By implementing innovative techniques such as composting or anaerobic digestion systems, organic wastes can be converted into nutrient-rich soil amendments or biogas for energy production. To illustrate this concept effectively, let’s analyze a three-column table showcasing different waste management approaches:
| Method | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Composting | Creates nutrient-rich soil | Requires proper monitoring |
| Anaerobic digestion | Produces biogas for renewable energy | Requires specific infrastructure |
| Incineration | Generates electricity or heat | Potential air pollution concerns |
By diversifying our waste management practices beyond traditional landfills and embracing more sustainable options like those mentioned above, we can work towards reducing our ecological footprint while simultaneously exploiting untapped resources hidden within our trash.
Transitioning effortlessly into the subsequent section about “Harnessing Energy from Waste,” we can recognize the potential of waste materials as a valuable energy source. By exploring innovative ways to utilize discarded resources, we can not only minimize environmental harm but also gain significant benefits in terms of renewable energy production.
Harnessing Energy from Waste
Building on the exploration of alternatives to landfills, this section delves into the concept of harnessing energy from waste. By adopting innovative technologies and practices, we can transform waste materials into valuable resources that contribute to sustainable energy production.
One example illustrating the potential of converting waste into energy is the case study of a city in Sweden. In this city, municipal solid waste is incinerated in specialized facilities equipped with state-of-the-art technology. The heat generated during combustion is used to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Additionally, the residual heat produced by the incineration process is captured and utilized for district heating systems, providing warmth to residential and commercial buildings throughout the city. This integrated approach not only reduces dependency on fossil fuels but also minimizes greenhouse gas emissions.
To fully comprehend the benefits of harnessing energy from waste, it is essential to consider various aspects:
-
Environmental Impact:
- Reducing landfill usage
- Decreasing methane emissions
- Lowering carbon footprint
-
Economic Viability:
- Generating revenue through electricity sales
- Creating job opportunities in waste-to-energy sector
- Attracting investments in renewable energy infrastructure
-
Resource Conservation:
- Recovering metals and other valuable materials from waste streams
- Preserving natural resources by using waste as a substitute fuel or raw material
-
Public Perception:
| Positive Aspects | Concerns | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced landfill space | Air pollution | Renewable energy source |
| Lower greenhouse gas emissions | Odor issues | Job creation |
| Recycling potential | Noise pollution | Revenue generation |
In conclusion, harnessing energy from waste offers numerous advantages ranging from environmental sustainability to economic prosperity. By implementing advanced technologies such as incineration coupled with efficient resource recovery, we can effectively address waste management challenges while contributing to the production of clean, renewable energy. Moving forward, it is crucial to continue exploring and investing in these innovative approaches to ensure a more sustainable future.
Managing Hazardous Materials Responsibly requires specialized knowledge and stringent measures for safe disposal and containment
Managing Hazardous Materials Responsibly
Harnessing Energy from Waste
In the previous section, we explored the various methods of harnessing energy from waste. Now, let us delve into the crucial aspect of managing hazardous materials responsibly in waste management practices.
One example highlighting the importance of responsible hazardous material management is the case of a chemical manufacturing plant located near a residential area. The plant had been disposing of its hazardous waste improperly for years, leading to severe environmental contamination and health risks for nearby residents. This case serves as a stark reminder that proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials are essential to safeguard both human health and the environment.
To ensure responsible management of hazardous materials, several key considerations must be taken into account:
-
Risk assessment: Conducting thorough risk assessments is vital to identify potential hazards associated with different types of waste materials. It allows for effective planning and implementation of appropriate safety measures during storage, transportation, treatment, or disposal processes.
-
Compliance with regulations: Adhering to local, national, and international regulations pertaining to hazardous waste management ensures legal compliance and minimizes negative impacts on public health and ecosystems. Regular monitoring and reporting systems should be established to verify adherence to these regulations.
-
Training and education: Providing comprehensive training programs for workers involved in handling hazardous materials promotes awareness about safe practices, emergency response procedures, and personal protective equipment usage. Educating the community about the dangers associated with improper handling or disposal can help prevent accidental exposures.
-
Collaboration between stakeholders: Establishing strong partnerships among government agencies, industries, non-profit organizations, research institutions, and communities fosters collective responsibility towards sustainable waste management solutions. Sharing knowledge, expertise, resources, and best practices contributes significantly to minimizing hazards posed by hazardous materials.
Table – Hazards Associated with Improper Hazardous Material Management
| Type | Impact |
|---|---|
| Chemical spills | Contamination of soil and water sources |
| Air emissions | Air pollution and respiratory health risks |
| Improper disposal | Soil, water, and air contamination |
| Worker exposures | Occupational hazards leading to injuries or illnesses |
In summary, responsible management of hazardous materials is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. By conducting thorough risk assessments, complying with regulations, providing training and education, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, we can mitigate the negative impacts associated with improper waste management practices.
Transitioning into the next section on Innovative Approaches to Recycling
Innovative Approaches to Recycling
Having explored the responsible management of hazardous materials, it is crucial to delve into innovative approaches that address the pressing issue of recycling. By embracing new techniques and technologies, waste management can be transformed into a more sustainable process. This section will examine some notable examples and strategies in recycling, highlighting their potential benefits towards environmental preservation.
One example of an innovative approach to recycling is the concept of upcycling. Unlike traditional recycling methods that involve breaking down materials for reuse, upcycling focuses on repurposing items without degradation or loss of quality. For instance, consider the case study of a company that transforms discarded plastic bottles into fashionable handbags. By creatively reimagining these materials instead of simply melting them down, they reduce both waste generation and carbon emissions associated with production processes. This exemplifies how upcycling not only diverts waste from landfills but also contributes to resource conservation.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions through decreased reliance on raw material extraction
- Preservation of natural resources by extending product lifecycles
- Mitigation of pollution by diverting waste from incinerators and landfills
- Creation of economic opportunities through job creation in green industries
Table: Environmental Benefits Comparison
| Recycling Method | Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Natural Resource Conservation | Pollution Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upcycling | Decreased | Extended | Diverted |
| Traditional | Minimal | Moderate | Partial |
As demonstrated in the table above, upcycling offers substantial advantages compared to traditional recycling methods regarding its positive effects on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving natural resources, and mitigating pollution.
In conclusion,
Through innovative approaches like upcycling, recycling has the potential to revolutionize waste management practices. By shifting towards these methods, society can not only minimize environmental harm but also create economic opportunities in green industries. The subsequent section will further explore another vital aspect of sustainable waste management: the role of composting.
Transition into the subsequent section:
Building upon the innovative approaches discussed thus far, it is important to consider the significant role that composting plays in achieving sustainable waste management.
The Role of Composting in Sustainable Waste Management
Recycling plays a crucial role in waste management, as it helps reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and promotes the conservation of valuable resources. This section will explore some innovative approaches to recycling, highlighting their benefits and potential impact on environmental sustainability.
To illustrate one such approach, let’s consider the case study of a city implementing a comprehensive recycling program. By providing residents with convenient access to recycling bins and educating them about proper sorting techniques, this city was able to significantly increase its recycling rates. As a result, the amount of waste sent to landfills decreased by 40%, reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with landfill decomposition. Additionally, the recycled materials were turned into new products or used as raw materials for manufacturing processes, leading to resource conservation.
When examining innovative approaches to recycling, several key factors emerge:
-
Technological advancements: The development of advanced sorting technologies allows for more efficient separation of recyclable materials from mixed waste streams. These technologies utilize sensors and automated systems to identify and sort different types of materials accurately.
-
Extended producer responsibility (EPR): EPR is an approach where manufacturers take responsibility for their products throughout their lifecycle, including post-consumer disposal. By implementing EPR programs, companies are incentivized to design products that are easier to recycle or reuse.
-
Collaborative partnerships: Effective recycling requires collaboration between various stakeholders such as municipalities, businesses, non-profit organizations, and educational institutions. Through these partnerships, resources can be pooled together to develop infrastructure and educational campaigns that promote recycling practices.
-
Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about the importance of recycling and how to properly dispose of recyclable materials is vital for increasing participation rates. Engaging communication strategies through social media platforms and community events can help raise awareness and encourage behavioral changes.
These approaches demonstrate how innovation in recycling can lead us towards a more sustainable future by minimizing waste generation while conserving valuable resources. By embracing such strategies, we can make significant progress in addressing the environmental challenges associated with waste management.
Transitioning into the next section on “The Role of Composting in Sustainable Waste Management,” exploring another facet of effective waste reduction and resource conservation without explicitly using the word “step,” we delve into a method that harnesses organic waste for beneficial purposes.
Strategies for Reducing Waste Generation
Building upon the importance of composting in sustainable waste management, it is crucial to explore strategies for reducing waste generation. By implementing effective waste reduction techniques, individuals and organizations can make significant contributions towards creating a cleaner and more environmentally friendly future.
One approach to waste reduction is through source separation or recycling. For instance, consider a hypothetical case study where an office building implements a comprehensive recycling program. This program includes designated bins for paper, plastic, glass, and metal waste throughout the premises. Employees are educated about what materials can be recycled and encouraged to actively participate in segregating their trash accordingly. This example demonstrates how simple yet impactful measures can lead to a substantial decrease in landfill-bound waste.
To further emphasize the significance of waste reduction, let us examine some key benefits associated with this practice:
- Environmental preservation: Each item that is not thrown away translates into conservation of natural resources such as water, energy, and raw materials.
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: By minimizing waste production, we prevent the release of harmful gases like methane from landfills, which contribute significantly to climate change.
- Financial savings: Implementing efficient waste reduction strategies often leads to decreased disposal costs for municipalities, businesses, and households alike.
- Promotion of a circular economy: Through proper waste management practices like recycling and reusing materials, we encourage resource efficiency by extending product lifecycles.
The following table illustrates different ways in which individuals and communities can reduce waste generation:
| Strategy | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Minimizing packaging | Opting for products with minimal or recyclable | Purchasing goods with eco-friendly packaging |
| packaging | ||
| Composting | Diverting organic wastes from landfills | Home composting systems |
| Recycling | Sorting and processing materials for reuse | Municipal recycling programs |
| Reusing | Extending the lifespan of objects through creative | Donating clothes and furniture instead of |
| reuse or donation | discarding them |
Incorporating these strategies into our daily lives, businesses, and policies can significantly contribute to waste reduction. By doing so, we move closer towards achieving sustainable waste disposal practices that prioritize environmental health and resource conservation.
To further promote sustainable waste disposal practices, let us delve into the importance of responsible waste management in the context of promoting a circular economy.
Promoting Sustainable Waste Disposal Practices
Transitioning from the previous section on strategies for reducing waste generation, it is crucial to explore the importance of promoting sustainable waste disposal practices. By adopting responsible methods of Waste Management, we can minimize environmental impacts and contribute to a healthier planet. To illustrate this point, let us consider a hypothetical case study in which a community implements sustainable waste disposal practices.
In this case study, a small town facing increasing waste generation decides to prioritize sustainability by implementing various measures. Firstly, they establish comprehensive recycling programs that encourage residents to separate recyclable materials from general waste. This initiative not only reduces landfill usage but also conserves valuable resources such as metals, plastics, and paper. Secondly, the town introduces composting facilities where organic waste is transformed into nutrient-rich soil additives. The resulting compost is then utilized in local gardens and farms instead of relying solely on chemical fertilizers.
To further emphasize the significance of promoting sustainable waste disposal practices, here are some key points worth considering:
- Effective education campaigns: Raising awareness about proper waste disposal techniques through educational initiatives can help change behaviors and foster a sense of responsibility among individuals.
- Collaboration with businesses: Encouraging industries and commercial establishments to adopt eco-friendly packaging materials and implement efficient recycling systems can significantly reduce their contribution to overall waste generation.
- Government support: Governments play a vital role in facilitating sustainable waste disposal practices by enacting legislation that promotes recycling and imposing penalties for improper waste management.
- Technological advancements: Investing in research and development efforts focused on innovative technologies for waste treatment can lead to more efficient processes and better utilization of resources.
Table 1 below summarizes the potential positive outcomes associated with promoting sustainable waste disposal practices:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced land pollution | Minimizing reliance on landfill sites decreases contamination risks. |
| Conservation of resources | Efficient recycling saves energy and preserves raw materials. |
| Improved air quality | Proper waste disposal avoids harmful emissions and odors. |
| Protection of ecosystems | Preventing the release of hazardous substances safeguards biodiversity. |
By adopting sustainable waste disposal practices, communities can significantly contribute to environmental preservation while reaping various benefits. In light of this, it becomes evident that addressing the challenges of waste-to-energy conversion is a pivotal next step towards achieving comprehensive and sustainable waste management solutions.
With an understanding of the importance of promoting sustainable waste disposal practices, we can now delve into the complexities associated with addressing the challenges of waste-to-energy conversion.
Addressing the Challenges of Waste-to-Energy Conversion
Transitioning from the previous section on promoting sustainable waste disposal practices, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with waste-to-energy conversion. While this approach has gained traction in recent years due to its potential for renewable energy generation and reduction of landfill space requirements, there are several obstacles that need to be addressed.
One example that highlights these challenges is the case of a municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration plant located in a densely populated urban area. Despite being equipped with advanced pollution control technologies, concerns over air emissions and their impact on public health have raised questions about the feasibility of such facilities near residential communities. This situation underscores the importance of finding balance between harnessing energy from waste while minimizing environmental and health risks.
To delve further into the complexities surrounding waste-to-energy conversion, let us consider some key factors:
-
Environmental Impacts: The process of converting waste into energy can result in various environmental impacts, including air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and residue management issues. Proper monitoring and mitigation strategies should be implemented to ensure that any adverse effects on ecosystems are minimized.
-
Economic Viability: Cost-effectiveness plays a significant role in determining the success of waste-to-energy projects. Factors such as capital investment, operational expenses, and revenue generated from energy sales must be carefully assessed to ensure economic viability over the long term.
-
Technological Advancements: Continued research and development efforts are necessary to improve existing waste-to-energy technologies and make them more efficient. Innovation in areas such as thermal treatment processes, gas cleaning systems, and resource recovery techniques will contribute towards enhancing overall sustainability.
-
Public Perception: Public acceptance is vital for successful implementation of waste-to-energy projects. Community engagement initiatives focusing on education, transparency, and addressing concerns can help foster trust among residents living near these facilities.
To gain a better understanding of these considerations and their implications, we present a table summarizing different aspects related to waste-to-energy conversion:
| Factors to Consider | Implications |
|---|---|
| Environmental impacts | Air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, residue management challenges |
| Economic viability | Capital investment, operational expenses, revenue generation from energy sales |
| Technological advancements | Improving efficiency of thermal treatment processes and resource recovery techniques |
| Public perception | Community engagement initiatives for trust-building and addressing concerns |
In summary, waste-to-energy conversion presents both opportunities and challenges. While it has the potential to contribute towards sustainable waste management practices and renewable energy production, careful attention must be given to environmental impacts, economic feasibility, technological advancements, and public perception. By effectively addressing these issues, we can further harness the benefits of waste-to-energy conversion while ensuring a more sustainable future.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on ensuring safe treatment of hazardous waste…
Ensuring Safe Treatment of Hazardous Waste
Having explored the challenges associated with waste-to-energy conversion, we now shift our focus towards another critical aspect of waste management – ensuring safe treatment of hazardous waste. To illustrate the importance of this topic, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving a chemical manufacturing plant.
Case Study Example:
Imagine a chemical manufacturing plant that produces various toxic substances as byproducts. The disposal and treatment of these hazardous wastes present significant challenges due to their potential harm to human health and the environment. This case study highlights the importance of implementing effective measures for safe handling and treatment.
The Importance of Proper Handling and Treatment:
To ensure the safe treatment of hazardous waste, it is crucial to establish robust protocols and guidelines. Here are some key considerations:
-
Classification and Segregation:
- Accurate classification allows for appropriate segregation based on hazard levels.
- Proper labeling ensures clear identification during storage, transportation, and disposal.
-
Storage Facilities:
- Adequate containment facilities minimize risks related to leaks or spills.
- Regular inspections help identify deteriorating conditions or breaches in safety protocols.
-
Transportation Protocols:
- Secure packaging prevents accidental exposure during transit.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements ensures adherence to safety standards.
-
Disposal Methods:
- Employing environmentally friendly methods such as recycling or neutralization whenever possible.
- Utilizing approved landfill sites equipped with necessary safeguards for long-term containment.
Table: Emotional Impact Visualization
| Benefit | Consequence | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Reduced pollution | Minimized health hazards |
| Negative | Increased compliance | Escalation of risks |
| Improved sustainability | Potential legal liability |
Effective waste management practices not only protect human health and the environment but also contribute to sustainable development. By implementing proper handling and treatment methods, we can reduce pollution levels, minimize health hazards, ensure compliance with regulations, and improve overall sustainability.
In light of these considerations, it is evident that safe treatment of hazardous waste should remain a priority in environmental technology. The measures highlighted in this section provide a foundation for effective waste management strategies. Through continued research and technological advancements, we can further enhance our ability to address the challenges associated with hazardous waste disposal while safeguarding our planet’s future well-being.

Comments are closed.