Tidal Energy: Harnessing Environmental Technology for Renewable Energy
Tidal energy, a form of renewable energy derived from the natural rise and fall of ocean tides, has garnered significant attention in recent years as an environmentally friendly solution to meet global energy demands. This article aims to explore the potential of tidal energy as a sustainable source of power generation by examining its advantages, challenges, and current applications. To illustrate this concept further, let us consider the case study of the MeyGen project located in Scotland’s Pentland Firth, which showcases how harnessing tidal energy can contribute to reducing carbon emissions while providing consistent electricity supply.
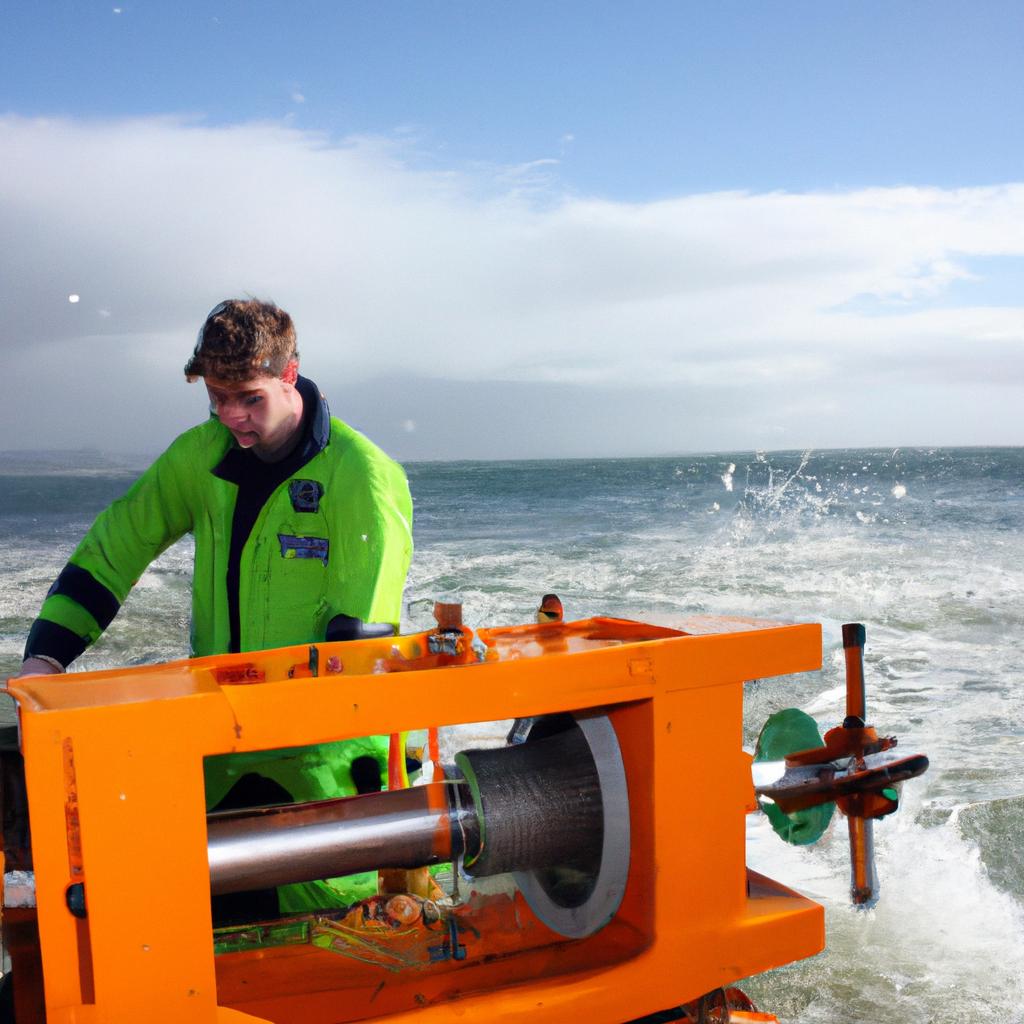
The MeyGen project serves as a prime example of utilizing tidal energy on a large scale. Situated between mainland Scotland and Orkney Islands, this pioneering endeavor has successfully deployed underwater turbines capable of converting kinetic energy from tidal currents into electrical power. As one of the largest tidal stream projects globally, MeyGen demonstrates the immense potential that lies within our oceans’ untapped resources. By exploiting predictable and continuous movements caused by gravitational forces exerted by celestial bodies such as the moon and sun, tidal energy offers an abundant and reliable source for generating clean electricity without detrimental environmental impacts associated with fossil fuel-based alternatives.
What is Tidal Energy?
Tidal Energy: Harnessing Environmental Technology for Renewable Energy
Tidal energy, also known as tidal power, is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the natural ebb and flow of ocean tides to generate electricity. It holds great potential as an alternative source of energy due to its reliability and predictability. To better understand the concept of tidal energy, let us consider a hypothetical case study.
Imagine a coastal region with a significant tidal range, where high and low tides occur twice daily. In this area, an underwater turbine system has been installed near the shore. As the tide rises, water flows into the turbines, causing them to rotate. The rotational motion then drives generators that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process continues during both flood (incoming) and ebb (outgoing) tides, maximizing power generation.
The utilization of tidal energy offers several advantages over conventional forms of power generation:
- Renewable: Tidal energy relies on the gravitational forces between Earth, Moon, and Sun; therefore, it is inexhaustible.
- Environmentally Friendly: Unlike fossil fuels or nuclear power plants which emit greenhouse gases or produce radioactive waste respectively, tidal energy does not contribute significantly to pollution or climate change.
- Predictable: The cyclic nature of tides allows for accurate forecasts regarding when power can be generated consistently.
- Sustainable Coastal Development: Implementing tidal projects can provide economic opportunities in coastal regions while minimizing environmental impact.
To visualize these benefits further:
| Advantages of Tidal Energy |
|---|
| Renewable |
These characteristics make tidal energy an attractive option for countries seeking clean and reliable sources of electricity generation without compromising their commitment to sustainability.
In transitioning to our next section about “How does Tidal Energy Work?”, we will explore how this captivating technology converts kinetic energy from ocean tides into usable electrical power.
How does Tidal Energy Work?
Harnessing the immense power of ocean tides, tidal energy has emerged as a promising source of renewable energy. One notable example of successful tidal energy implementation is the MeyGen project in Scotland’s Pentland Firth. The project aims to generate clean electricity by utilizing the strong currents flowing between the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea.
Tidal energy works through various mechanisms that harness the kinetic energy generated by moving water. Firstly, there are tidal barrages, which involve constructing large dams across estuaries or bays with high tidal ranges. As the tide rises and falls, water flows through turbines installed within these structures, generating electricity in both directions. Secondly, there are tidal stream generators that operate similarly to wind turbines but underwater. They capture the kinetic energy from tidal currents and convert it into electrical energy using rotors connected to generators.
The utilization of tidal energy offers several advantages over conventional fossil fuel-based sources:
- Renewable and Sustainable: Tidal energy relies on predictable natural cycles caused by gravitational forces exerted by celestial bodies such as the moon and sun.
- Low Environmental Impact: Unlike traditional methods of power generation, tidal technology produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions and pollution.
- Energy Security: Tidal resources are indigenous and not subject to geopolitical risks associated with imported fuels.
- Economic Opportunities: The development of tidal projects can create job opportunities in manufacturing, construction, maintenance, and research sectors.
Table – Comparison of Tidal Energy with Other Renewable Sources
| Renewable Source | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Solar Power | Abundant sunlight availability; scalability |
| Wind Power | Cost-effectiveness; rapid deployment potential |
| Hydroelectricity | Large-scale production capability; long lifespan |
Transitioning seamlessly into discussing another aspect related to tidal energy, it becomes evident that this eco-friendly form of power generation holds numerous advantages over traditional non-renewable alternatives. By further exploring its benefits for both humans and nature, we can gain a deeper understanding of why tidal energy is gaining momentum as an attractive solution for sustainable electricity production. In the subsequent section, we will examine the advantages of tidal energy and its potential impact on our society and environment.
Advantages of Tidal Energy
Tidal Energy: Harnessing Environmental Technology for Renewable Energy
Now let us delve deeper into this fascinating process and explore how it works.
To better understand the concept, consider a hypothetical scenario where a tidal power plant is located along the coast of Wales. As the tide rises, water enters large turbines positioned strategically within an estuary. These turbines are similar to windmill blades but designed to rotate when water flows through them. The upward movement of the tide causes these turbines to spin, activating generators that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. When the tide recedes, gates close to prevent seawater from flowing back out, ensuring continuous energy production during both high and low tides.
Harnessing tidal energy offers numerous advantages over conventional forms of energy generation. Here are some key benefits:
- Clean and renewable: Tidal energy is a clean source of power as it produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution. By utilizing natural resources such as ocean tides, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change impacts.
- Predictable and reliable: Unlike solar or wind power which rely on weather conditions, tidal patterns follow predictable cycles based on lunar gravitational forces. This reliability allows for accurate forecasting and efficient planning of energy generation.
- Long lifespan: Tidal power plants have a longer operational life compared to other renewable technologies like wind farms or solar panels due to their robust design and minimal exposure to external elements.
- Job creation potential: The development and maintenance of tidal power infrastructure require skilled laborers and technicians, creating employment opportunities in coastal communities.
These advantages make tidal energy an attractive option for sustainable power generation, contributing towards global efforts in combating climate change while fostering economic growth.
In the subsequent section about “Challenges in Harnessing Tidal Energy,” we will explore the obstacles faced in fully realizing the potential of this renewable energy source. By addressing these challenges, we can pave the way for a future where tidal energy plays a significant role in our global energy mix.
Challenges in Harnessing Tidal Energy
Harnessing the power of tidal energy offers numerous benefits for sustainable electricity generation. By utilizing the natural ebb and flow of ocean tides, this renewable energy source has proven to be a promising alternative to traditional forms of power generation. To further understand the advantages of tidal energy, let us consider an example case study.
One notable example is the MeyGen project in Scotland, which aims to harness the immense potential of tidal currents in the Pentland Firth. With its innovative underwater turbines, this project can generate clean and reliable energy from tides that are known to reach speeds of up to 8 knots (approximately 9 miles per hour). This case study demonstrates how tidal energy initiatives have the potential to contribute significantly towards meeting global renewable energy targets.
The advantages associated with harnessing tidal energy include:
- Renewable and predictable: Unlike other renewable sources like wind or solar, tides are highly predictable and occur twice a day without fail. This predictability allows for efficient planning and integration into existing electrical grids.
- Environmentally friendly: Tidal energy does not produce harmful emissions or pollutants during operation, reducing carbon footprint and minimizing environmental impacts compared to conventional fossil fuel-based power plants.
- High energy density: The kinetic force generated by moving water masses is incredibly powerful, resulting in high-energy yields even from relatively small-scale installations.
- Job creation and economic growth: Investment in tidal energy projects stimulates local economies through job creation, infrastructure development, and increased tourism opportunities.
To illustrate these advantages visually:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable | Tidal currents occur reliably twice daily, ensuring a consistent supply of renewable energy. |
| Environmentally Friendly | Tidal energy production emits no greenhouse gases or air pollutants during operation. |
| High Energy Density | The kinetic force from moving water masses results in significant amounts of usable electricity. |
| Job Creation and Economic Growth | Tidal energy projects stimulate local economies through job creation and increased tourism opportunities. |
In conclusion, the advantages of tidal energy are evident in its predictability, environmental friendliness, high energy density, and potential for economic growth. By harnessing this renewable resource, we can move towards a more sustainable future.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Current Applications of Tidal Energy,” it is crucial to explore how these advantages have been put into practice.
Current Applications of Tidal Energy
Tidal Energy: Harnessing Environmental Technology for Renewable Energy
Challenges in Harnessing Tidal Energy have been acknowledged, yet the current applications of this technology demonstrate its potential to overcome these obstacles and provide sustainable energy solutions. One notable example is the MeyGen tidal energy project located off the coast of Scotland. This innovative venture harnesses the power of tides in the Pentland Firth, one of the world’s most powerful tidal channels. By employing a combination of underwater turbines, it has successfully generated clean electricity that can power thousands of homes.
The implementation of tidal energy projects offers several advantages over traditional fossil fuel-based sources. Firstly, tidal energy is renewable and inexhaustible since it relies on predictable patterns caused by gravitational forces from celestial bodies. Secondly, it produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants during operation, thereby minimizing environmental impacts and combating climate change. Moreover, tidal energy projects contribute to job creation and economic growth through investment in research and development, manufacturing, installation, operations, and maintenance.
To further emphasize the benefits of tidal energy utilization:
- Reduction in dependence on non-renewable resources
- Enhanced grid stability due to consistent tide cycles
- Preservation of marine ecosystems by avoiding harmful extraction techniques
- Mitigation of coastal erosion through controlled water flows
Table 1 showcases some key comparative factors between conventional fossil fuels and tidal energy sources:
| Factors | Conventional Fossil Fuels | Tidal Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | High | Zero |
| Resource Availability | Finite | Infinite |
| Environmental Footprint | Significant | Minimal |
| Reliance on Imports | Yes | No |
In light of these advantages and comparisons, it becomes evident that tapping into the immense potential offered by tides holds significant promise for future sustainability efforts. The next section will explore how advancements in technology and ongoing research are leading to further growth and efficiency in the utilization of tidal energy, ensuring a brighter future for renewable energy generation.
Future Potential of Tidal Energy will be discussed in the subsequent section, exploring emerging technological advancements and research initiatives that pave the way for increased sustainability and energy independence.
Future Potential of Tidal Energy
Transition from the previous section H2:
Having explored the current applications of tidal energy, we now turn our attention to its future potential. With advancements in technology and increasing global demand for renewable energy sources, tidal energy holds promise as a sustainable solution for meeting our growing energy needs.
Future Potential of Tidal Energy
To better understand the immense possibilities that lie ahead, let us consider a hypothetical scenario. Imagine a coastal region with strong tidal currents, where an underwater turbine farm is established. This farm harnesses the power of these tides to generate electricity on a large scale. The success of this project not only meets the local community’s energy requirements but also contributes surplus power back into the grid system, reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based generation methods.
As we look towards the future development of tidal energy, several factors contribute to its attractiveness as a viable source of renewable power:
- Predictable and Reliable: Unlike solar or wind energy, which are subject to fluctuations based on weather conditions, tidal patterns can be accurately predicted years in advance. This reliability allows for more efficient planning and integration into existing electrical grids.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Tidal turbines cause minimal disruption to marine ecosystems compared to other forms of renewable energy such as offshore wind farms. By utilizing vertical movement rather than horizontal rotation, they minimize harm to marine life while still capturing substantial amounts of kinetic energy.
- Longevity and Durability: Tidal turbines have an average lifespan exceeding 20 years, making them a reliable long-term investment option for governments and private entities alike. Additionally, their location below water surfaces protects them from extreme weather events that may affect above-ground structures.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The establishment and operation of tidal energy projects create employment opportunities within coastal communities and stimulate economic growth through increased investments in infrastructure development.
| Benefits of Tidal Energy |
|---|
| Predictable Power Generation |
| Job Creation and Economic Growth |
In conclusion, the future potential of tidal energy lies in its ability to provide a reliable and sustainable source of electricity with minimal environmental impact. With increasing advancements in technology and growing global demand for renewable energy, further investment and research are needed to unlock its true potential. By leveraging the predictable nature of tides, minimizing harm to marine ecosystems, ensuring durability, and stimulating economic growth, tidal energy holds substantial promise as we strive towards a greener and more sustainable future.

Comments are closed.