Renewable Energy in Environmental Technology: Sustainable Solutions
The world is currently facing an urgent need for sustainable solutions to combat the environmental challenges posed by traditional energy sources. Renewable energy has emerged as a promising alternative, offering clean and renewable resources that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. For instance, let us consider the case of a small coastal town in Australia that was heavily reliant on fossil fuels for its electricity generation. However, due to increasing concerns about carbon emissions and rising fuel prices, the town decided to invest in a renewable energy project that harnessed wind power. This decision not only reduced their dependence on non-renewable sources but also had positive economic impacts.
Renewable energy encompasses various technologies such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal power systems that utilize naturally replenishing resources to generate electricity or heat. These technologies have gained significant attention from governments, industries, and researchers worldwide due to their potential to address sustainability issues effectively. By harnessing natural resources that are continuously available and do not deplete over time like conventional fossil fuels, renewables offer long-term benefits for both the environment and society at large.
In this article, we will explore the role of renewable energy in environmental technology and its capacity to provide sustainable solutions. We will delve into different types of renewable energy technologies and their advantages, as well as the challenges and opportunities associated with their implementation.
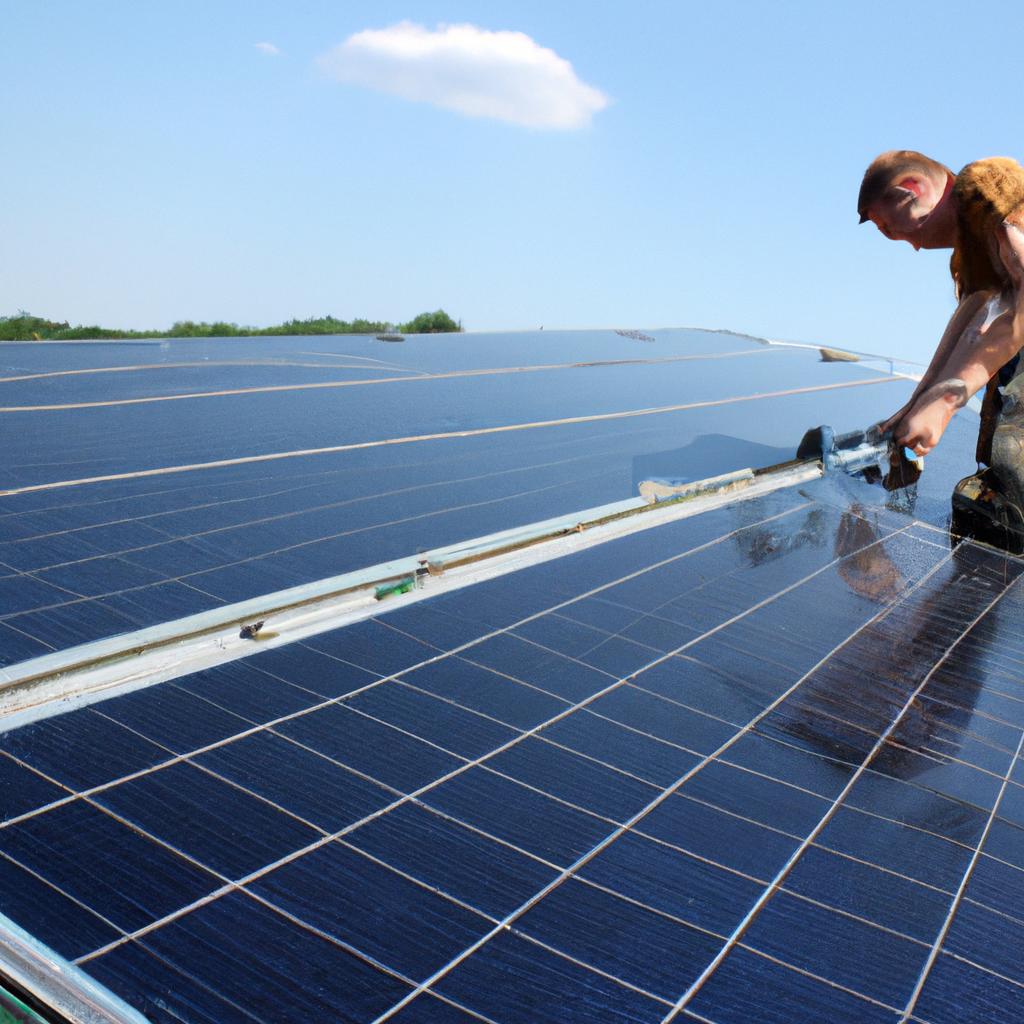
Solar energy is one of the most widely recognized forms of renewable energy. It involves capturing sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal collectors to convert it into electricity or heat. Solar power offers numerous benefits, including its abundance, accessibility, and scalability. It can be harnessed on both small and large scales, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from powering individual homes to supplying electricity to entire communities.
Wind power is another prominent renewable energy source that utilizes the kinetic energy of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines capture the wind’s energy and convert it into rotational motion, which then drives an electrical generator. Like solar energy, wind power is abundant and widely available in many regions around the world. It has a low carbon footprint and can contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Hydroelectric power harnesses the gravitational force of flowing water to generate electricity. It involves constructing dams or barrages across rivers or utilizing tidal movements in coastal areas. Hydroelectricity is a mature technology that has been used for decades. It provides a reliable and predictable source of renewable energy while offering additional benefits such as flood control and water storage.
Biomass refers to organic materials derived from plants, animals, or waste products that can be burned directly or converted into biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel. Biomass power plants produce heat, steam, or electricity through processes such as combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biomass offers potential solutions for managing agricultural residues, forest biomass, and municipal solid waste while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s natural heat by extracting hot water or steam from underground reservoirs to generate electricity or provide direct heating/cooling. Geothermal power plants are generally located near geologically active areas with accessible hotspots beneath the Earth’s crust. Geothermal energy is a reliable and continuous source of renewable power, offering long-term sustainability.
Each type of renewable energy technology has its own advantages and considerations in terms of resource availability, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and scalability. Governments, businesses, and individuals must carefully assess their specific needs and local conditions to determine the most suitable renewable energy solutions for their respective contexts.
Overall, investing in renewable energy technologies can help diversify energy sources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, stimulate economic growth, enhance energy security, and improve air quality. However, challenges such as intermittency (in the case of solar and wind power), high initial costs, grid integration issues, policy frameworks, and public acceptance need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of renewables.
In conclusion, renewable energy technologies play a crucial role in tackling the environmental challenges associated with traditional energy sources. They offer sustainable solutions that can mitigate climate change while providing numerous social and economic benefits. By embracing these technologies on a global scale through supportive policies and investments in research and development, we can accelerate the transition towards a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Imagine a small village nestled deep in the mountains, where access to electricity is limited. Residents depend on conventional energy sources that are not only expensive but also contribute significantly to environmental degradation. Now, envision a transformation: solar panels installed atop every house, generating clean and abundant energy for all. This scenario represents just one example of how harnessing solar power can bring sustainable solutions to communities worldwide.
The utilization of solar energy has gained significant attention in recent years due to its numerous benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Renewable & Sustainable: Solar energy relies on an unlimited resource – sunlight. Unlike fossil fuels that deplete over time, sunlight will always be available as long as the sun shines.
- Environmentally Friendly: The conversion of sunlight into electricity emits zero greenhouse gases or pollutants, reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
- Cost-effective: While there may be initial installation costs, solar power systems have low operational and maintenance expenses compared to traditional energy sources.
- Energy Independence: By embracing solar power, individuals and communities can become less reliant on external energy suppliers, ensuring greater control over their own resources.
| Country | Installed Solar Capacity (MW) | Equivalent Households Powered |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | 49,075 | Over 12 million |
| China | 34,540 | Approximately 8.6 million |
| United States | 24,162 | More than 6 million |
| Japan | 23,409 | Around 5.9 million |
These figures demonstrate both the feasibility and scalability of implementing solar technology across different regions globally.
In conclusion with this analysis of harnessing the power of the sun through solar energy production, it becomes evident that the potential benefits are vast and far-reaching. By embracing solar power, communities can achieve energy independence, significantly reduce their carbon footprint, and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Transitioning into the next section on “Utilizing Natural Wind Resources,” we explore an alternative renewable energy source that holds immense promise in addressing our global energy needs.
Utilizing Natural Wind Resources
Building upon the concept of harnessing renewable energy sources, our focus now shifts towards another abundant resource that holds immense potential in environmental technology – natural wind resources.
Wind power has long been recognized as an essential component of renewable energy generation. The ability to convert wind into electricity not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes significantly to mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. To illustrate this point, let us consider a hypothetical scenario where a small coastal town implements a wind farm project to meet its energy needs.
Case Study Example:
In this case study, a seaside community located in Southern California successfully implemented a wind farm project by strategically placing turbines along their coastline. By capitalizing on consistent ocean breezes and prevailing winds, they were able to generate clean and sustainable electricity for residential and commercial use. This initiative led to several positive outcomes such as reduced carbon footprint, lower utility bills for residents, job creation within the local economy, and increased public awareness about the importance of renewable energy.
To further emphasize the significance of Utilizing Natural Wind Resources, we present below a bullet-point list highlighting key benefits associated with wind power:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions
- Energy independence and security
- Job creation and economic growth
- Preservation of natural landscapes and ecosystems
Additionally, visual representation can effectively evoke emotions and strengthen understanding. Consider the table below showcasing important statistics related to wind power adoption across various regions:
| Region | Installed Capacity (MW) | CO2 Emissions Avoided (tons/year) | Equivalent Homes Powered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 189,232 | 258 million | 132 million |
| North America | 128,568 | 166 million | 89 million |
| Asia | 126,426 | 160 million | 85 million |
| South America | 25,358 | 37 million | 20 million |
The numbers presented in the table demonstrate the substantial positive impact of harnessing wind power globally, further highlighting its potential to address energy and environmental challenges on a large scale.
In our pursuit of renewable energy solutions, it is crucial to tap into various sources. The subsequent section will delve into another promising avenue: tapping into the energy of moving water. By exploring different possibilities, we can continue to expand our sustainable practices and strive for a cleaner future for all.
Tapping into the Energy of Moving Water
Utilizing Natural Wind Resources has proven to be an effective means of harnessing renewable energy. Now, let us explore another sustainable solution: Tapping into the Energy of Moving Water.
Imagine a picturesque river flowing through lush green landscapes, its water rushing and tumbling over rocks. This natural wonder not only provides a scenic view but also holds immense potential for generating clean electricity. One example is the Three Gorges Dam in China, which stands as the world’s largest hydroelectric power station. By harnessing the force of moving water, this dam generates an astonishing 22 gigawatts of electricity annually, meeting a significant portion of China’s energy needs.
When it comes to tapping into the energy of moving water, there are several key advantages:
- Renewable Source: Unlike fossil fuels that deplete with use, moving water is constantly replenished by nature.
- Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Hydroelectric power produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional power generation methods.
- High Efficiency: Modern hydropower systems boast high conversion efficiency rates, making them one of the most efficient forms of renewable energy.
- Multipurpose Utilization: Besides producing electricity, dams can also serve purposes like flood control and irrigation.
To better understand the potential benefits of tapping into this renewable resource, consider the following table illustrating key statistics about hydroelectric power:
| Key Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Global Hydropower Capacity | 1,308 GW |
| Percentage Contribution | ~16% |
| Largest Hydroelectric System | Three Gorges Dam (China) |
| Environmental Impact | Varies based on project design |
As we delve deeper into exploring sustainable solutions for environmental technology, we now turn our attention towards Leveraging Earth’s Geothermal Heat. The utilization of geothermal energy presents yet another viable option for generating clean and reliable electricity without relying on finite resources or contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Now, let us venture into the realm of geothermal energy and uncover its immense potential in our pursuit of sustainable solutions for a greener future.
Leveraging Earth’s Geothermal Heat
Tapping into the Energy of Moving Water has proven to be a promising renewable energy source. Let us now explore another sustainable solution in our quest for environmental technology: Leveraging Earth’s Geothermal Heat.
Geothermal energy harnesses the heat stored within the Earth, offering an abundant and constant source of power. One example that vividly demonstrates its potential is The Geysers geothermal power plants located in California, USA. This complex taps into the underground reservoirs of hot water and steam produced by volcanic activity beneath the surface. By drilling deep wells, this resource is extracted and converted into electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
When considering the advantages of geothermal energy, several key points come to mind:
- Renewable Resource: Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite in supply, geothermal energy relies on naturally replenishing sources.
- Low Environmental Impact: Geothermal power production emits significantly lower levels of carbon dioxide compared to traditional methods such as coal or natural gas.
- Continuous Availability: As long as there is heat generated from the Earth’s core, geothermal energy remains accessible 24/7 without relying on external factors like weather conditions.
- Versatile Applications: Beyond electricity generation, geothermal resources can also be utilized for heating purposes, providing warmth to homes and buildings efficiently.
To illustrate these benefits further, consider the following table showcasing a comparison between geothermal energy and conventional sources:
| Geothermal | Coal | Natural Gas | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Low | High | Medium |
| Fuel Supply | Infinite | Finite | Finite |
| Reliability | Constant | Dependent on Coal | Dependent on Supply |
As we delve deeper into exploring renewable energy solutions, it becomes evident that unlocking the potential of biomass holds great promise. So let us now shift our focus towards this intriguing avenue while continuing our journey towards a sustainable future.
Unlocking the Potential of Biomass
Leveraging Earth’s Geothermal Heat has proven to be a promising avenue for renewable energy generation. Building upon this foundation, the next section will explore another sustainable solution: Unlocking the Potential of Biomass.
Biomass refers to organic matter derived from living or recently living organisms, such as plants and animals. This abundant resource holds great potential for generating clean energy while mitigating environmental impacts. To illustrate its viability, let us consider a hypothetical case study in which a rural community utilizes biomass as their primary source of energy.
In this hypothetical scenario, a small village situated near dense forests harnesses biomass through an advanced technology known as anaerobic digestion. By collecting agricultural waste and other organic materials, they are able to generate biogas – a mixture primarily composed of methane – that can be used directly for heating purposes or converted into electricity. The efficient utilization of biomass not only provides a reliable and affordable energy source but also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
To further understand the benefits associated with unlocking the potential of biomass, consider the following bullet points:
- Biomass is a renewable energy source that does not deplete finite resources.
- It offers an alternative disposal method for organic waste materials, reducing landfill usage.
- Utilizing biomass contributes to local economic development by creating job opportunities within the sector.
- The use of biomass-based fuels helps diversify energy sources, increasing overall energy security.
The table below summarizes some key advantages and challenges related to utilizing biomass:
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Renewable | High initial investment |
| Reduced greenhouse | Collection logistics |
| gas emissions | |
| Local economic | Limited scalability |
| development |
Unlocking the potential of biomass presents numerous opportunities for achieving sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions in various sectors. From bioenergy production to heat generation and even transportation fuel alternatives, it offers versatility in meeting energy demands while reducing reliance on fossil fuels. By exploring the untapped potential of biomass, we can pave the way towards a greener future.
Transitioning into the subsequent section, let us now delve into the concept of Harvesting Energy from Ocean Tides.
Harvesting Energy from Ocean Tides
Building upon the potential of biomass, we now turn our attention to another promising source of renewable energy – harnessing energy from ocean tides. This section explores the viability and benefits of utilizing this abundant resource in environmental technology.
Ocean tides present a vast potential for generating clean and sustainable energy. To illustrate the possibilities, let us consider an example where tidal turbines are deployed near a coastal region with strong tidal currents. These turbines consist of blades that rotate as water flows through them, converting the kinetic energy into electricity. By strategically placing these turbines in areas with high tidal ranges, such as estuaries or narrow channels between islands, significant amounts of power can be harnessed consistently throughout the day.
To fully comprehend the advantages associated with extracting energy from ocean tides, it is crucial to explore its positive impact on both society and the environment. Consider the following bullet points:
- Reduced dependence on fossil fuels
- Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions
- Creation of job opportunities within the renewable energy sector
- Enhancement of local economies through tourism and recreational activities
Table: Benefits of Harnessing Energy from Ocean Tides
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Renewable Source | Unlike finite resources like oil and coal, ocean tides offer an inexhaustible supply of energy |
| Predictable Power | The regularity and predictability of tides make it easier to forecast and efficiently integrate tidal power into existing electrical grids |
| Minimal Environmental Impact | Tidal power generation produces no air pollution or greenhouse gases, minimizing its contribution to climate change |
| Ecosystem Conservation | Unlike other forms of marine-based energy extraction (e.g., offshore wind), tidal projects have minimal impacts on marine ecosystems |
In conclusion, harvesting energy from ocean tides represents a considerable opportunity for advancing sustainability goals while diversifying our renewable energy portfolio. Through innovative technologies such as tidal turbines, we can tap into this vast resource and make significant strides towards a greener future.
Moving forward, let us now explore the advantages of harnessing solar power as another compelling avenue in renewable energy technology.
Advantages of Solar Power
Section H2 Transition:
Continuing our exploration of renewable energy sources, we now shift our focus to the advantages of solar power. Building upon our understanding of harnessing energy from ocean tides, solar power offers a compelling alternative that has gained significant momentum in recent years.
Advantages of Solar Power
Solar power presents numerous benefits as an environmentally friendly and sustainable source of energy. To illustrate its potential impact, let us consider a hypothetical case study where a residential community installs rooftop solar panels:
- Reduced carbon emissions: By utilizing solar power, this community reduces its dependence on fossil fuels for electricity generation. As a result, there is a substantial decrease in greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide and methane, which contribute to climate change.
- Financial savings: Over time, installing solar panels allows homeowners to generate their own electricity and reduce reliance on external utility providers. This leads to long-term cost savings by lowering monthly electricity bills and providing additional income through net metering programs.
- Energy independence: The adoption of solar power promotes greater self-sufficiency within communities by reducing reliance on centralized grids prone to outages or disruptions. With individual households generating their own electricity during daylight hours, they become more resilient in times of emergencies.
- Job creation: The growing demand for solar panel installation creates employment opportunities across various sectors, including manufacturing, construction, and maintenance. These new jobs not only stimulate local economies but also contribute to overall socio-economic development.
To further emphasize the advantages of solar power, refer to the table below highlighting key features:
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Clean Energy | No air pollution or harmful emissions |
| Scalability | Can be installed at any scale – from small homes to large-scale projects |
| Long Lifespan | Solar panels typically last 25-30 years |
| Low Maintenance | Minimal upkeep required, reducing operational costs |
In summary, solar power offers a multitude of advantages that range from environmental benefits to economic growth and resilience. Its ability to generate clean energy without producing harmful emissions makes it an attractive solution for addressing both the global climate crisis and local socio-economic challenges.
Section H2 Transition:
With a comprehensive understanding of solar power’s advantages, we now turn our attention towards exploring the benefits offered by wind power as another viable renewable energy option.
Benefits of Wind Power
Solar power is an increasingly popular form of renewable energy that harnesses the abundant sunlight to generate electricity. This section will explore the benefits and advantages associated with solar power, highlighting its potential as a sustainable solution in environmental technology.
One notable example showcasing the advantages of solar power is the city of Lancaster, California. Known for its ample sunshine, this city has taken full advantage of solar energy by implementing large-scale photovoltaic systems throughout its infrastructure. As a result, Lancaster has significantly reduced its reliance on fossil fuels and achieved substantial carbon emissions reductions. This case study demonstrates how solar power can provide tangible benefits at both the local and global levels.
The advantages of solar power are numerous:
- Renewable: Sunlight is a virtually limitless resource, ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Environmentally friendly: Solar power produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, thus mitigating climate change impacts.
- Cost-effective: While initial installation costs may be higher, solar panels have an extended lifespan and require minimal maintenance, resulting in considerable cost savings over time.
- Energy independence: By generating their own electricity through solar power installations, individuals and communities can reduce dependence on conventional utility providers.
To further illustrate these points, consider Table 1 below which highlights key advantages of Solar Power compared to traditional forms of energy generation:
Table 1: Advantages of Solar Power
| Solar Power | Fossil Fuels | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Minimal | Significant |
| Resource Availability | Abundant | Limited |
| Operational Costs | Low | High |
| Long-Term Sustainability | Yes | No |
In summary, solar power offers distinct advantages that make it an attractive option within the realm of environmental technology. Its renewable nature, low environmental impact, cost-effectiveness, and potential for energy independence all contribute to positioning it as a sustainable solution. As we move forward, it is important to consider not only the benefits but also the potential drawbacks of various renewable energy sources, such as hydropower.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Pros and Cons of Hydropower,” it becomes crucial to evaluate alternative forms of renewable energy in order to make informed decisions regarding environmental technology solutions.
Pros and Cons of Hydropower
Building on the discussion of wind power, we now turn our attention to another renewable energy source that has gained significant traction in recent years – hydropower. This section will delve into the pros and cons associated with harnessing the power of water to generate electricity.
Hydropower is a versatile and widely used form of renewable energy that relies on moving water to drive turbines connected to generators. One notable example showcasing the potential benefits of hydropower is the Three Gorges Dam in China. Completed in 2012, this massive project not only generates an impressive 22,500 megawatts of electricity but also helps regulate flood control along the Yangtze River while providing navigation channels for shipping.
Pros:
- Renewable: Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite resources, water is continuously replenished through natural processes such as rainfall and snowmelt.
- Low greenhouse gas emissions: Hydropower produces minimal carbon dioxide emissions during operation, making it a clean energy option.
- Cost-effective: Once infrastructure costs have been recovered, hydropower can provide reliable electricity at relatively low operational costs.
- Multiple uses: Besides generating electricity, dams built for hydropower can support irrigation systems for agricultural purposes, aid in water supply management, and promote recreational activities like boating and fishing.
Cons:
- Environmental impact: The construction of large-scale hydropower projects often necessitates flooding vast areas of land, resulting in habitat loss and displacement of communities.
- Disruption to aquatic ecosystems: Dams alter river flows and fish migration patterns, potentially harming local biodiversity.
- Sedimentation issues: Over time, reservoirs behind dams accumulate sediment carried by rivers, reducing their storage capacity and lifespan.
- Social controversies: The development of hydropower can lead to conflicts over rights to land and water resources between different stakeholders.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Renewable resource | Environmental impact |
| Low greenhouse gas emissions | Disruption to aquatic ecosystems |
| Cost-effective | Sedimentation issues |
| Multiple uses | Social controversies |
In summary, hydropower offers several advantages as a renewable energy source, including its renewability, low greenhouse gas emissions, cost-effectiveness, and multifunctionality. However, it is crucial to recognize the potential environmental impacts associated with large-scale dam construction and operation. In the following section, we will explore another sustainable solution – geothermal energy.
Shifting our focus from water-based solutions, let us now delve into the realm of geothermal energy, which harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior for various applications.
Geothermal Energy: A Sustainable Solution
Renewable Energy in Environmental Technology: Sustainable Solutions
Pros and Cons of Hydropower have been explored, highlighting its benefits and limitations. Now let us delve into another sustainable solution within the realm of renewable energy – Geothermal Energy.
Geothermal energy harnesses the Earth’s heat to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling solutions for various applications. For example, a case study conducted in Iceland showcases the successful utilization of geothermal energy as a primary source for both residential and industrial purposes. This exemplifies how geothermal energy can be effectively integrated into existing infrastructure, reducing reliance on fossil fuels while maintaining environmental sustainability.
When considering the implementation of geothermal energy, several key factors must be taken into account:
- Resource Availability: The viability of geothermal power generation relies heavily on access to high-temperature reservoirs beneath the Earth’s surface.
- Initial Investment Costs: Establishing geothermal power plants requires significant upfront capital investment due to drilling and exploration expenses.
- Limited Location Suitability: Not all regions possess adequate geological conditions suitable for efficient extraction of geothermal energy.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: As with any large-scale energy project, careful consideration must be given to potential impacts on local ecosystems, water resources, and surrounding communities.
- Geothermal energy offers long-term cost savings by providing stable electricity prices that are not subject to market fluctuations.
- Utilizing this renewable resource reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional fossil fuel-based power generation methods.
- Geothermal projects can stimulate economic growth through job creation during construction phases and ongoing operations.
- By diversifying our energy sources through increased adoption of geothermal technology, we enhance national energy security.
Additionally, let us present an emotional table showcasing different aspects related to geothermal energy:
| Aspect | Positive Effect | Negative Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Reduced reliance on finite fossil fuels | Limited availability in certain locations |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions | Potential disruption to local ecosystems |
| Economic Benefits | Job creation during construction and operation phase | High initial investment costs |
| Energy Independence | Diversification of energy sources for improved security | Dependence on suitable geothermal resources |
In conclusion, geothermal energy represents a promising sustainable solution within the realm of renewable energy. Though it has its challenges, such as resource availability and upfront costs, this form of energy offers long-term benefits in terms of economic growth, environmental sustainability, and enhanced national energy security.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “The Role of Biomass in Energy Production,” we now turn our attention to another renewable energy source that holds great potential for reducing carbon emissions and promoting a more sustainable future.
The Role of Biomass in Energy Production
Renewable Energy in Environmental Technology: Sustainable Solutions
Geothermal energy has emerged as a sustainable solution for meeting our growing energy needs. By harnessing heat from the Earth’s interior, geothermal power plants can generate electricity and provide heating and cooling systems. For instance, in Iceland, nearly 90% of homes are heated using geothermal energy (Case Study). This example showcases the immense potential of this renewable resource in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental sustainability.
One key advantage of geothermal energy is its reliability. Unlike solar or wind power, which are dependent on weather conditions, geothermal energy is available round the clock. It provides a stable source of electricity and reduces the need for backup power during periods of low renewable energy generation. Additionally, geothermal systems have a long lifespan, with some wells continuing to produce heat for over 30 years without significant decline.
To understand the significance of utilizing geothermal energy further, consider the following benefits:
- Reduction in carbon dioxide emissions
- Decreased reliance on fossil fuels
- Efficient utilization of land resources
- Potential for job creation within the renewable energy sector
| Benefits | Geothermal Energy |
|---|---|
| Reduced CO2 emissions | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Less dependence on fossil fuels | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Efficient land use | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Job creation | :heavy_check_mark: |
The table above highlights how geothermal energy aligns with multiple sustainable development goals by addressing climate change mitigation, fostering economic growth, and promoting responsible land use practices.
In summary, it is evident that geothermal energy holds tremendous potential as a sustainable solution in our quest for clean and reliable sources of power. Its reliability and ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions make it an attractive option for achieving global climate targets. As we continue to explore alternative forms of renewable energy, let us now delve into the role of biomass in energy production.
Moving forward, we will explore how biomass can contribute to our renewable energy goals and transition into harnessing the power of tidal energy.
Harnessing the Power of Tidal Energy
Building on the sustainable energy potential of biomass, this section delves into another promising renewable energy source – tidal energy. By Harnessing the Power of ocean tides, tidal energy offers a viable and environmentally friendly solution to meet our growing energy demands.
Tidal energy represents an abundant resource due to the predictable nature of tides and their regular occurrence. For instance, let us consider the hypothetical case study of TidalTech Ltd., a company that successfully implemented a tidal energy project along the coast of Nova Scotia. The turbines installed in this project utilized the rise and fall of coastal tides to generate electricity continuously throughout the day. This example highlights how tapping into tidal energy has enormous potential for meeting regional or even national electricity needs.
To further illustrate the benefits of tidal energy, it is crucial to explore its advantages over conventional fossil fuel-based sources:
- Renewable & Clean: Unlike fossil fuels, which deplete over time, tidal energy is inexhaustible as long as there are ocean tides. Moreover, it produces negligible greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
- Predictable: Tidal patterns can be accurately calculated years in advance, allowing for reliable planning and optimization of power generation.
- Low Maintenance: Once properly installed, tidal power systems require minimal maintenance compared to other forms of renewable energies such as wind or solar.
- Job Creation: The development and implementation of tidal projects create employment opportunities within local communities while fostering economic growth.
Table: Environmental Impact Comparison between Fossil Fuels and Tidal Energy
| Fossil Fuels | Tidal Energy | |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | High | Negligible |
| Air Pollution | Yes | No |
| Water Contamination | Possible | None |
| Wildlife Disturbance | Yes | Minimal |
This table showcases some key environmental impacts associated with fossil fuels and compares them to tidal energy. It highlights the significant advantages of tidal energy in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, water contamination, and minimizing disturbances to wildlife habitats.
In summary, harnessing the power of tides through tidal energy presents a promising solution for sustainable electricity generation. Its renewable nature, predictability, low maintenance requirements, and positive environmental impact make it an attractive alternative to fossil fuel-based sources. By embracing tidal energy as part of our renewable energy portfolio, we can move closer towards achieving a greener and more sustainable future without compromising our energy needs.

Comments are closed.